Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has been diagnosed . For most patients, these three words are initially incomprehensible. And the situation is over – it’s not like coughing and having bronchitis or having severe abdominal pain and ulcers. Complaints are present, but it is difficult for the patient to formulate them or relate them to a specific part of his body.
Acute myeloid leukemia – what is it?
The disease is a type of cancer – a malignant – disease of the blood.
Leukemia means that a certain type of tumor cells – blasts – are found in the patient’s blood . They originate from early forms of blood cells.
Myeloid is leukemia, which refers to the bone marrow where blood cells are produced. The blasts also accumulate there and subsequently enter the bloodstream.
The disease is acute because it develops rapidly – the diagnosis is made within the first few days to weeks after the onset of symptoms, and treatment begins immediately after diagnosis.
The symptoms
Acute leukemia is a malignant disease. It is expressed in the uncontrolled rapid proliferation of abnormal cells – blasts, which occupy more and more of the bone marrow. In this regard, the latter can not function normally, that is – fails to ensure the required amount of normal blood cells, with all the consequences for the patient.
Expressions of bone marrow failure are:
- Anemia – which is expressed by pallor, fatigue, shortness of breath and palpitations;
- More common infections – especially lung infections , due to impaired production of immune cells;
- Bleeding – due to reduced production of cells involved in blood clotting – platelets. This will be, for example, bleeding from the mucous membranes – gums and nose, as well as skin – bruises with minimal or no impact.
Blasts can accumulate not only in the bone marrow but also elsewhere in the body. With this they can cause pain – on the bones, an increase in the size of the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, testicles. In rare cases, the blasts may penetrate both the cerebrospinal fluid and the spinal cord and brain or their meninges.
Which patients is affected?
Acute myelodine leukemia can occur at any age, but only about 25% of cases are in people under 25 years of age. The incidence of the disease increases after 40 years, with an average age of diagnosis of about 65 years.
A specific cause of the disease can rarely be identified. So far, the following risk factors for its development have been described:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation;
- Exposure to benzene;
- Chemotherapy for other malignancies;
- Preliminary presence of other bone marrow diseases catpo myelodysplastic syndrome;
- Presence of a sibling or parent affected by acute myeloid leukemia .
In any case, this is not a contagious or inherited disease.
Diagnosis
As it turned out, it should be placed as soon as possible, because treatment can begin in the first hours after diagnosis.
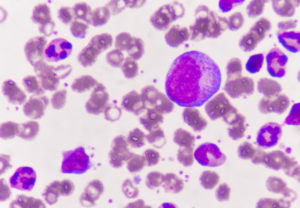
The most basic test, such as a complete blood count ( PKC ), may show abnormalities in normal blood cell counts, but this is not required. In PKK they are counted by hardware. DCC is the differential blood count in which a doctor examines a drop of blood spread on a glass under a microscope. In this way, he can detect the blasts characteristic of the disease.
This leads to the most important test – that of the bone marrow . It is usually sufficient to perform aspiration – taking blood from the bone marrow and examining it under a microscope. All this can be realized within a few hours.
Additional genetic and immunological tests should be performed to determine the exact type of myeloid leukemia, which is important for treatment planning. In some cases, cerebrospinal fluid analysis is also performed. If an invasion of structures and organs in the body is suspected, an imaging examination – a scanner – can be performed.
Echocardiography is not a diagnostic test, but it is important to perform it before starting treatment.
The material is informative and cannot replace consultation with a doctor. Be sure to consult a doctor before starting treatment.