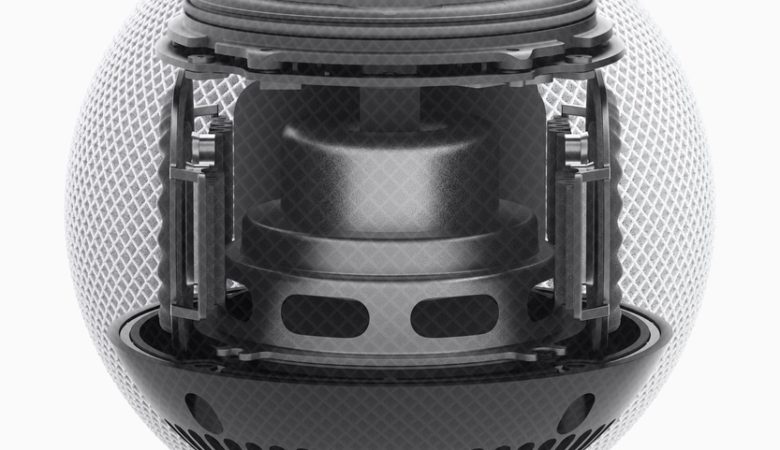
Several nuclear power plants are currently still active around world Here you can find out how exactly nuclear power plants work and the devastating disadvantages they have.
How does a nuclear power plant work?
A nuclear power plant (also known as a nuclear power plant or AKW) generates electrical energy from nuclear energy. The technology is based on nuclear fission: An atomic nucleus is split into several nuclei, which releases large amounts of energy.
This phenomenon was discovered in 1938 by the German chemists Otto Hahn and Friedrich Wilhelm Strassmann. A year later, Lise Meitner, one of Hahn’s employees, was able to physically explain the enormous amounts of energy released for the first time.
This is how nuclear energy is converted into electricity in a nuclear power plant:
- In a nuclear power plant, the fission takes place in the so-called nuclear part of the power plant. This is where the nuclear reactor is located.
- The energy gained is used to generate thermal energy in the form of water vapor.
- In the conventional part of the nuclear power plant, this steam is fed into a steam turbine. This drives a generator so that the thermal energy is converted into electrical energy.
- The electrical energy can be passed on to individual households as electricity.
Advantages of nuclear power plants
The first nuclear power plant was commissioned in Russia in 1954 . From this point in time, states built numerous nuclear power plants worldwide – especially in the 1960s, many nuclear power plants were opened. At first, the power plants were seen as a groundbreaking success: they had finally found a seemingly inexhaustible and clean way to generate energy.

Nuclear power plants are relatively inexpensive: one kilogram of uranium can generate many more kilowatt hours of electricity than, for example, oil. However, the cost of nuclear power is rising steadily as new nuclear power plants are becoming more and more expensive – solar and wind power, on the other hand, are significantly cheaper . The costs for the final storage of nuclear waste and possible nuclear accidents then come on top of that.
If you compare them to the generation of energy from fossil fuels (such as gas , coal and oil), nuclear power plants appear at first glance to be much more environmentally friendly. This is because they produce lower amounts of carbon dioxide.
This popular argument from nuclear power plant proponents: Inside, however, can be refuted: Because the fuel rods of the nuclear power plant have to be processed and the uranium mined – and this creates large amounts of CO2 . Renewable energy sources are a much more sustainable option.
The great danger: nuclear disasters
On April 26, 1986 we were shown a devastating disadvantage of the apparently “safe” nuclear power plants. That day the Chernobyl nuclear disaster occurred . The reactor of a nuclear power plant exploded, causing its graphite shell to burn and enormous amounts of radioactivity were released into the earth’s atmosphere.
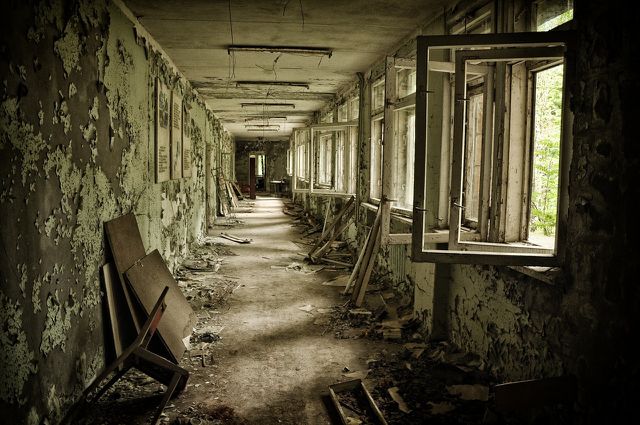

In the immediately affected areas in Ukraine and Belarus, some of the people are still suffering from the consequences of the worst-case scenario. These range from severe thyroid and cancer diseases to miscarriages and deformities. How many people died as a result of this devastating accident will never be exactly proven. Radiation doctors and scientists assume 30,000 to 60,000 fatalities from cancer alone.
The nuclear disaster in Fukushima in March 2011 is another example of the uncontrollable dangers and consequences of nuclear power plants.
Other disadvantages of nuclear power plants
But the nuclear power plants are facing other unsolved problems: To this day, it is still not known how to properly dispose of radioactive waste . This nuclear waste is highly radioactive for a long time and is therefore extremely harmful to humans, animals and nature.
The so – called half – life indicates how long it takes for a certain amount of a radioactive emitter to decay halfway. For the substance technetium-99 this time is 210,000 years, for neptunium-237 the value is 2.1 million years. You can read more about this topic in our article ” Nuclear waste disposal: the unsolved problem of nuclear energy “.
Also provide Nuclear Power Plant critics to internal consider that nuclear power stations a target for terrorist attacks could be. Such an attack would trigger a global crisis and could have devastating health and environmental consequences.
A supposed advantage of nuclear power plants is that nuclear power generation costs so little. What is forgotten, however, is that nuclear reactors only have a limited lifespan . New nuclear reactors have to be built again and again in order to guarantee a constant number and thus a stable power supply. This always results in new costs. Large amounts of money have also been spent to date to research and develop nuclear energy.
Last but not least, uranium is a scarce resource , which contrary to initial opinions is not inexhaustible. According to a press release from Greenpeace in 2006, forecasts indicated that global uranium supplies would be exhausted by around 2071.